
Currently, most thermal power plants in China use the traditional chemical coagulation and sedimentation process for treating wet desulfurization wastewater, but the overall operational rate is very low. After treatment by the traditional system, the concentrations of Suspended Solids (SS) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in the desulfurization wastewater remain high, and the system cannot remove Cl⁻. Due to the high Cl⁻ content, the treated wastewater cannot be reused. Considering environmental requirements and economic benefits, using advanced treatment technologies to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is an inevitable trend in wastewater treatment.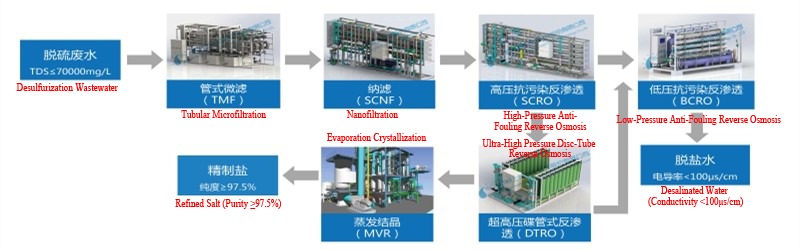
Traditional Process: Wastewater generated from the limestone-gypsum wet flue gas desulfurization process contains a large amount of impurities, primarily consisting of high concentrations of suspended solids, high chloride content, high salinity, and high concentrations of heavy metals. Direct discharge of these substances into natural water systems would inevitably cause serious environmental pollution. The current traditional treatment method in China involves neutralizing the desulfurization wastewater with alkali, causing most heavy metals to form precipitates. A coagulant is then added to thicken the precipitate into sludge, which is sent to a slag yard for disposal.
Although the desulfurization wastewater after the aforementioned traditional physicochemical treatment can basically meet the requirements for standard discharge, its reuse potential is very limited.
YHDE - ZLDS Zero Liquid Discharge Technology
1.Tubular Microfiltration (TMF): Uses unique composite membrane tubes. The PVDF membrane can effectively cross-link with the inner wall of the PVDF support tube or be embedded into the PE support tube wall, forming a strong bond with the support tube. This allows the membrane tubes to operate under high operating and backwash pressures, achieving extremely high solids removal efficiency and membrane flux, thereby reducing the system footprint. Removes hardness, silica, and turbidity. Silica removal rate can exceed 90%.
2.Nanofiltration (SCNF): A pressure-driven membrane separation process that falls between reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration, retaining particles of nanometer size. Compared to ultrafiltration or reverse osmosis, nanofiltration is less effective at rejecting monovalent ions and organic substances with a molecular weight below 200, but has a high removal rate for divalent or multivalent ions and organic substances with a molecular weight between 200 and 500. Removes divalent ions and separates salts in the feed water. Divalent ion removal rate can exceed 95%.
3.High-Pressure Fouling-Resistant Reverse Osmosis (SCRO): Reverse osmosis is a pressure-driven membrane separation process that separates the solvent from a solution. Pressure applied to the feed side exceeds the osmotic pressure, causing the solvent to move reverse to the natural osmosis direction. As a result, purified solvent (permeate) is obtained on the low-pressure side, and a concentrated solution (concentrate) is obtained on the high-pressure side. Desalinates, concentrates, and reduces the volume of the feed water. Desalination rate can exceed 95%.
4.Ultra-High Pressure Disc-Tube Reverse Osmosis (DTRO): The DTRO high-pressure membrane is the core component for separating fresh water from impurities. Made from polymer materials, aromatic polyamide is selected for the disc membrane material due to its excellent chemical properties. After initial pressurization by the feed pump and filtration through the cartridge filter, the wastewater enters the high-pressure pump. The circulation pump provides high flow to meet the flow velocity requirements on the DTRO membrane surface. The liquid flows in a forward/reverse "S" direction through the disc channels. Fine particles and dissolved ions are retained on the concentrate side, and the permeate is collected as clean filtrate. Further concentrates and reduces the volume of the concentrate from the previous stage. The TDS of the concentrate can reach 12%.








Henan Yuanhede Industrial Technology Co., Ltd.
East Industrial Park, Yuzhou City, Henan Province, China.
(+86)139 3822 7726
info@yhdegroup.com
www.yhdegroup.com